YOLOV8+HID实现自动瞄准
本篇文章记录了一个从“视觉感知 → 决策与控制 → 外设执行”的完整闭环实践:以 YOLOv8 完成特定目标检测训练与端侧部署(ONNX→RKNN),通过 HDMI-IN + GStreamer/OpenCV 采集画面,在 Linux Gadget 框架下模拟 HID 鼠标,实现基于检测结果的自动瞄准与点击。内容覆盖数据集准备与训练、模型转换与推理、HID 设备创建与事件发送,以及稳定性相关的平滑、死区、节流等工程化细节,力求给出一套可复现、可调参的端到端方案。自动瞄准根本就是小菜一碟!
适读人群包括:
- 需要在嵌入式平台做实时目标检测与人机自动化联动的开发者
- 对 USB Gadget/HID、GStreamer、边缘 AI 推理有一定基础的开发者。
- 建议具备 Conda/PyTorch 基础、Linux 终端操作经验,并预先完成 RKNN 环境搭建与 HDMI/OTG 连接测试。
1.YOLOV8模型部署
在开始前学习《AI进阶应用》中的《目标检测模型部署》,这一小节详细描述了模型获取和模型转换部署。那么如果识别特定目标,就需要准备数据集使用YOLOV8进行模型训练。
- YOLOV8模型训练参考工程:百度网盘链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1cLRsPlBA8K7KJja6XtHrxw?pwd=k4yq 提取码: k4yq
1.1 模型训练
模型训练建议使用GPU加速训练,下面教程是基于Window下使用Conda创建环境,如果您的主机不是Windows或者下面的教程无法在您的主机上实现,可在自行在网上检索YOLOV8 模型训练相关教程。
1.安装AnaConda
进入AnaConda的官网https://www.anaconda.com/ ,下载AnaConda安装包。
2.搭建YOLOV8环境
打开Anaconda Prompt终端,创建Python3.11的Conda环境,输入
conda create -n yolov8-gpu-test python=3.11
安装pytorch和cuda
conda install pytorch torchvision torchaudio pytorch-cuda=12.1 -c pytorch -c nvidia -y
安装yolov8依赖库
pip install ultralytics==8.2.0
3.获取yolov8 v8.2.0源码
git clone -b v8.2.0 https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics.git
4.准备数据集
这里以AimLab数据集为例,这里使用已经标注好的数据集aimlab Dataset > Overview。这里可使用我提前下载好的数据集:
百度网盘链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1H3-BO9ros8aLhWAiVCOj1g?pwd=xn87 提取码: xn87
如果您想使用自己的数据集进行训练,可以下载 X-AnyLabeling 完成标注,标注完成后的数据转换成yolov8官方支持的训练数据格式。
在yolov8项目同级目录下,新建datasets目录,在这个目录下新建AimLab目录,存放数据集文件,目录结构如下:
$ tree
.
|-- datasets
| `-- AimLab
| |-- test
| |-- train
| |-- valid
|-- ultralytics-8.2.0
| |-- CITATION.cff
| |-- CONTRIBUTING.md
| |-- LICENSE
| |-- README.md
| |-- README.zh-CN.md
| |-- docker
| |-- docs
| |-- examples
| |-- mkdocs.yml
| |-- pyproject.toml
| |-- runs
| |-- tests
| |-- ultralytics
| `-- yolov8n.pt
将数据集的data.yaml重命名aimlab.yaml为并放到ultralytics/cfg/datasets/目录下。修改aimlab.yaml数据集描述文件,指定数据集路径:
path: ../../datasets/AimLab
train: train/images
val: valid/images
test: test/images
nc: 1
names: ['targets']
5.训练模型
yolo detect train data=ultralytics/cfg/datasets/aimlab.yaml model=yolov8n.pt epochs=500 imgsz=640
训练完成后可以在runs/detect/train*/weights目录下看到训练完成的模型文件。以下为训练过程图片:

6.导出ONNX模型
安装ONNX库:
pip install onnx
pip install onnxruntime
pip install onnxsim
指定导出ONNX模型
yolo export model=runs/detect/train/weights/best.pt format=onnx imgsz=640
导出完成后可以在runs\detect\train\weights\best.onnx看到模型文件。
1.2 模型转换
模型转换需要使用RKNN的模型转换环境,如果之前没用搭建过RKNN环境,请参考《AI进阶应用》的《RKNN环境搭建》章节。
- 模型示例:链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1MmielydsG2t9hyHwoqA3rg?pwd=t355 提取码: t355
将训练完成并导出的ONNX模型传输至~/Projects/rknn_model_zoo/examples/yolov8/model目录下,使用如下命令进行模型转换
#进入yolov8模型转换目录
cd ~/Projects/rknn_model_zoo/examples/yolov8/python
#执行模型转换
python3 convert.py ../model/best.onnx rk3576
执行完成后可以在model目录下看到转换后的yolov8.rknn模型文件。
1.3 端侧推理
1.将~/Projects/rknn_model_zoo/examples/yolov8/python/yolov8.py源码中的
CLASSES = ("person", "bicycle", "car","motorbike ","aeroplane ","bus ","train","truck ","boat","traffic light",
"fire hydrant","stop sign ","parking meter","bench","bird","cat","dog ","horse ","sheep","cow","elephant",
"bear","zebra ","giraffe","backpack","umbrella","handbag","tie","suitcase","frisbee","skis","snowboard","sports ball","kite",
"baseball bat","baseball glove","skateboard","surfboard","tennis racket","bottle","wine glass","cup","fork","knife ",
"spoon","bowl","banana","apple","sandwich","orange","broccoli","carrot","hot dog","pizza ","donut","cake","chair","sofa",
"pottedplant","bed","diningtable","toilet ","tvmonitor","laptop ","mouse ","remote ","keyboard ","cell phone","microwave ",
"oven ","toaster","sink","refrigerator ","book","clock","vase","scissors ","teddy bear ","hair drier", "toothbrush ")
修改为:
CLASSES = ("target")
2.将需要推理的图片拷贝到当前目录下。
2.执行推理代码:
python3 yolov8.py --model_path ../model/yolov8.rknn --target rk3576 --img_folder ./ --img_show
运行效果图如下:
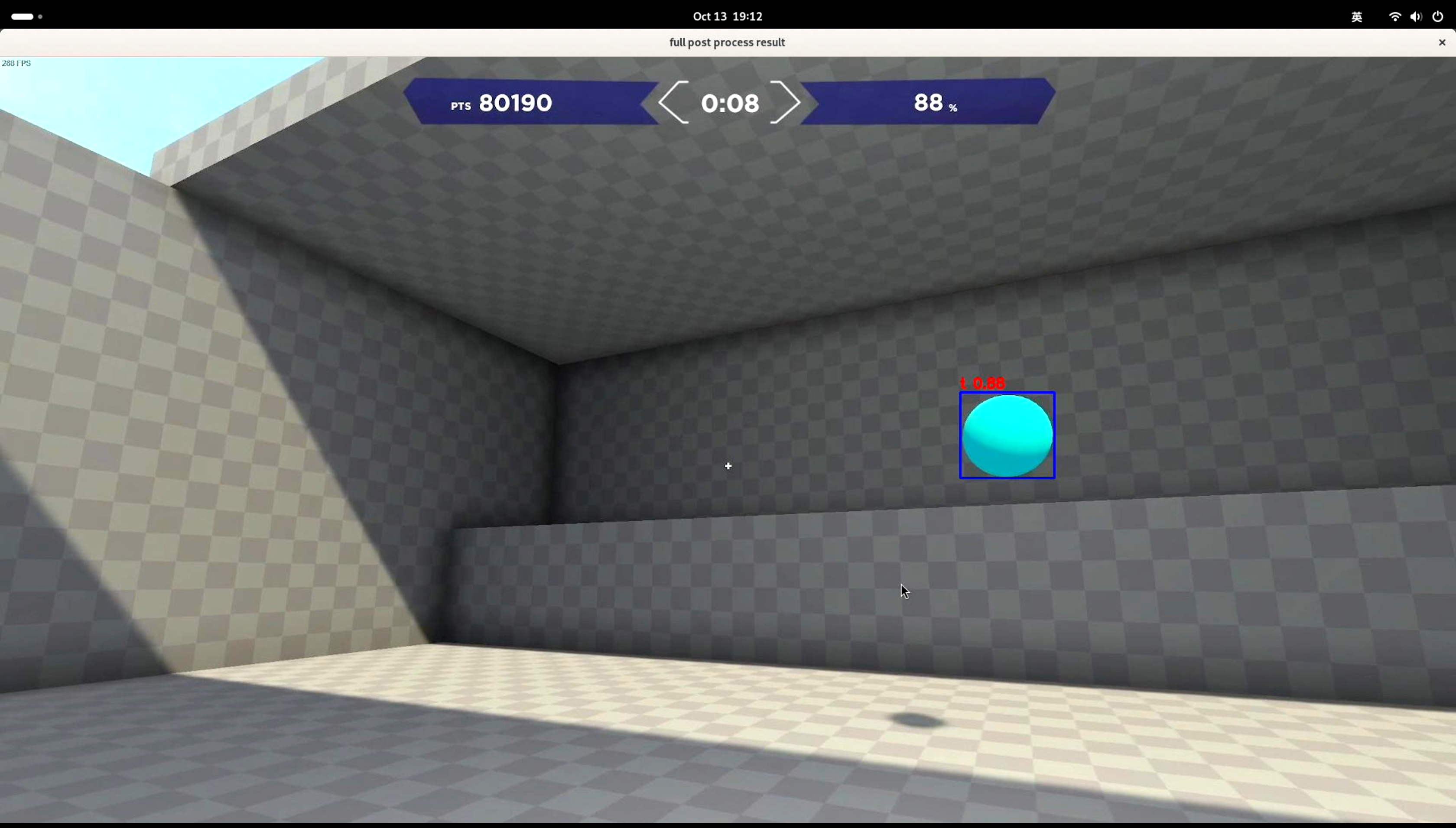
2.模拟键鼠
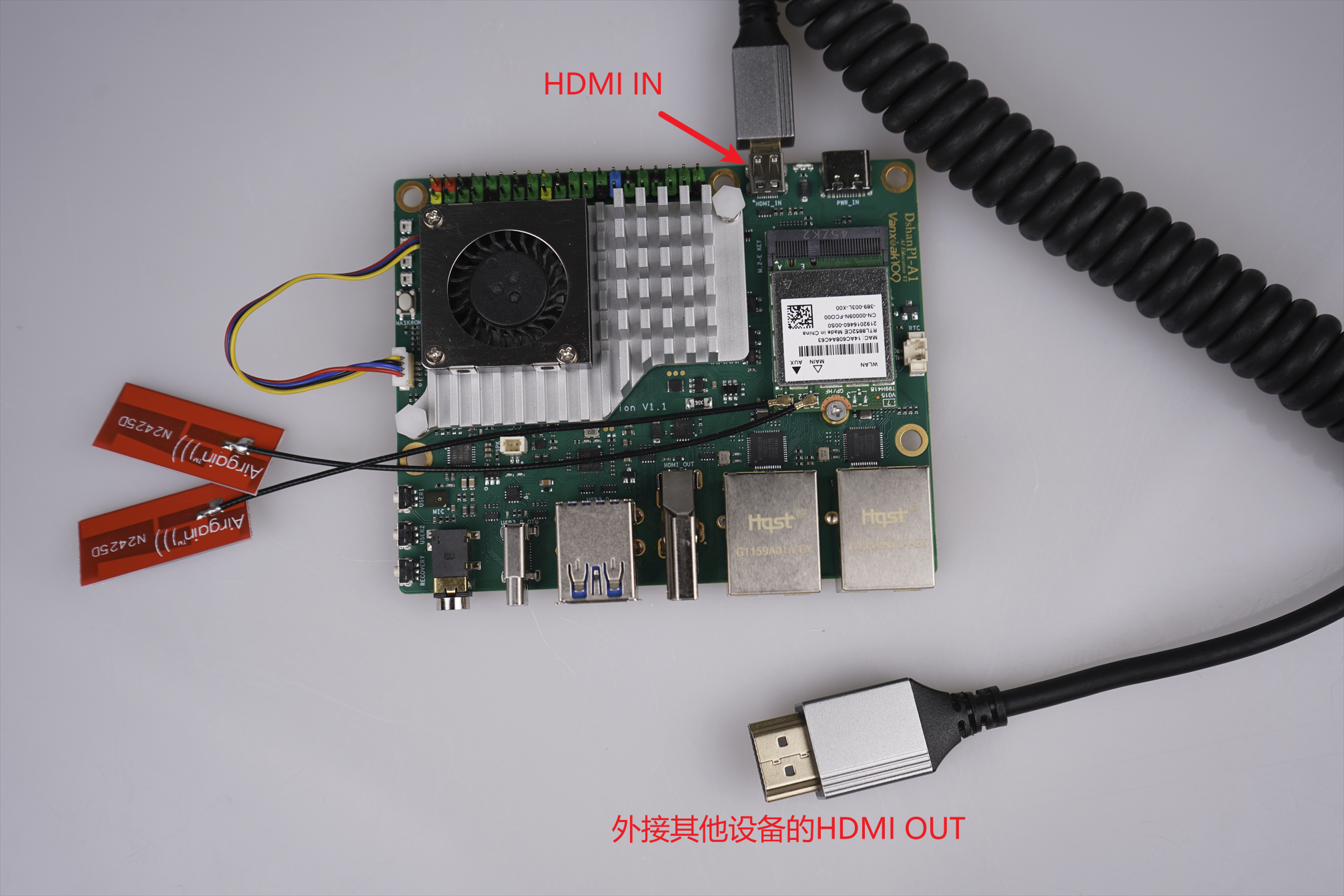
开始前请提前将DshanPI A1的OTG使用Type-C数据线连接至电脑端。
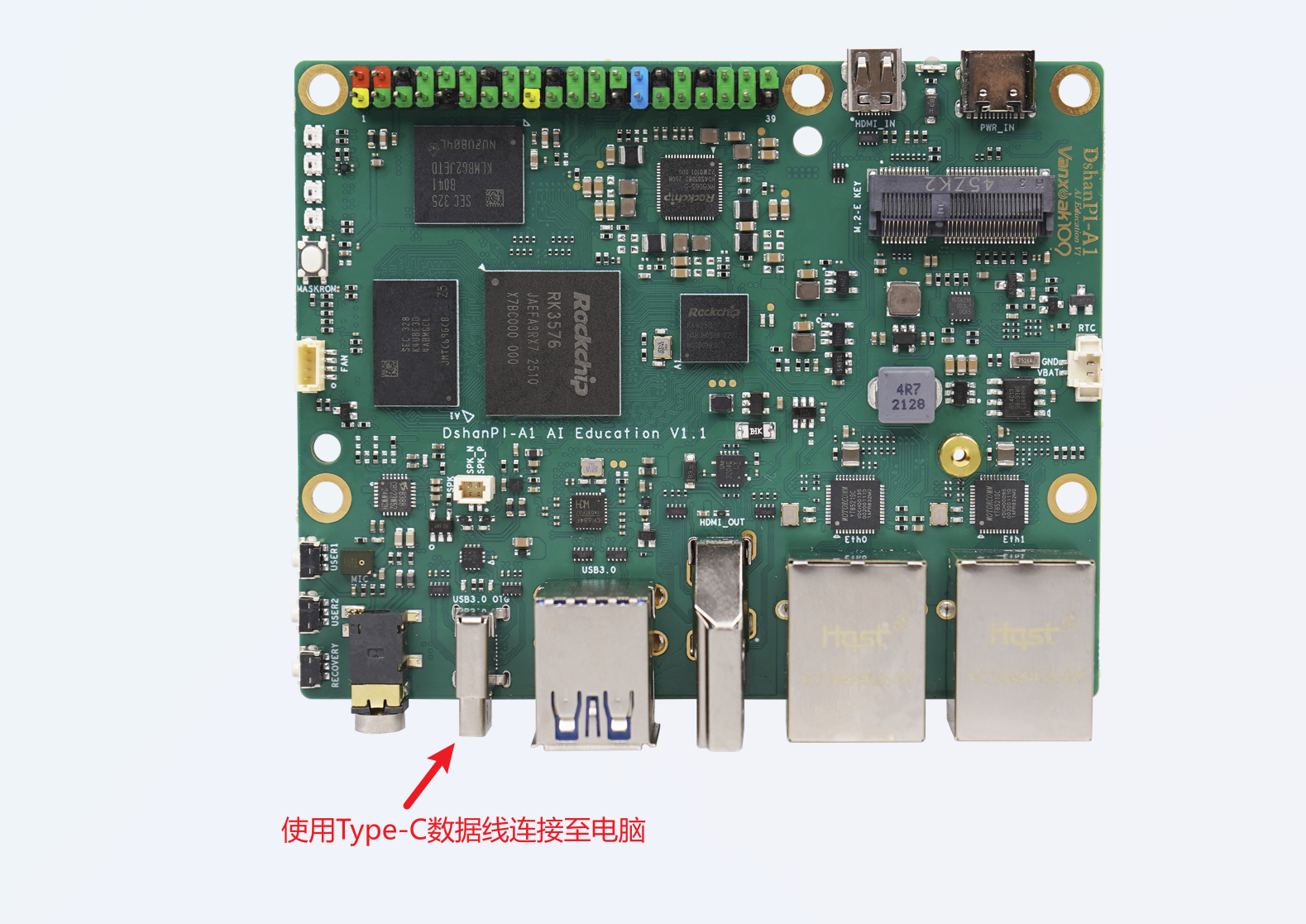
2.1 HID模拟
1.安装依赖库:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install libusbgx-dev
# 加载核心 gadget 框架
sudo modprobe libcomposite
2.新建脚本目录
sudo mkdir -p /opt/hid-gadget
新建脚本文件init.sh:
HID 脚本
#!/bin/bash
# absolute.sh - Create an absolute mouse HID gadget
GADGET_DIR=/sys/kernel/config/usb_gadget/g1
# 清理旧 gadget
if [ -d "$GADGET_DIR" ]; then
echo "Cleaning up old gadget..."
echo "" > $GADGET_DIR/UDC 2>/dev/null
rm -rf $GADGET_DIR
fi
# 创建 gadget
mkdir -p $GADGET_DIR
cd $GADGET_DIR
# 设置 USB ID
echo 0x1d6b > idVendor # Linux Foundation
echo 0x0104 > idProduct # Custom
echo 0x0100 > bcdDevice
echo 0x0200 > bcdUSB
# 创建字符串描述符
mkdir -p strings/0x409
echo "0123456789" > strings/0x409/serialnumber
echo "Test Manufacturer" > strings/0x409/manufacturer
echo "Absolute Mouse" > strings/0x409/product
# 创建配置
mkdir -p configs/c.1
mkdir -p configs/c.1/strings/0x409
echo "Config 1: HID" > configs/c.1/strings/0x409/configuration
echo 120 > configs/c.1/MaxPower
# 创建 HID 函数
mkdir -p functions/hid.usb0
echo 1 > functions/hid.usb0/protocol # Mouse
echo 2 > functions/hid.usb0/subclass # Boot Interface Subclass
echo 8 > functions/hid.usb0/report_length # 报告长度(字节)
# report descriptor
echo -ne '\x05\x01\x09\x02\xa1\x01\x09\x01\xa1\x00\x05\x09\x19\x01\x29\x03\x15\x00\x25\x01\x75\x01\x95\x03\x81\x02\x75\x05\x95\x01\x81\x03\x05\x01\x09\x30\x09\x31\x15\x00\x26\xff\x7f\x75\x10\x95\x02\x81\x02\xc0\xc0' > functions/hid.usb0/report_desc
# 绑定 HID 函数到配置
ln -s functions/hid.usb0 configs/c.1/
# 激活 gadget
UDC_NAME=$(ls /sys/class/udc | head -n 1)
if [ -z "$UDC_NAME" ]; then
echo "Error: No UDC found! Make sure your board supports USB OTG."
exit 1
fi
echo $UDC_NAME > UDC
增加可执行权限:
sudo chmod +x /opt/hid-gadget/init.sh
运行脚本:
sudo /opt/hid-gadget/init.sh
增加权限:
sudo chmod 666 /dev/hidg0
运行完成后可以在电脑端的设备管理器中看到鼠标设备。
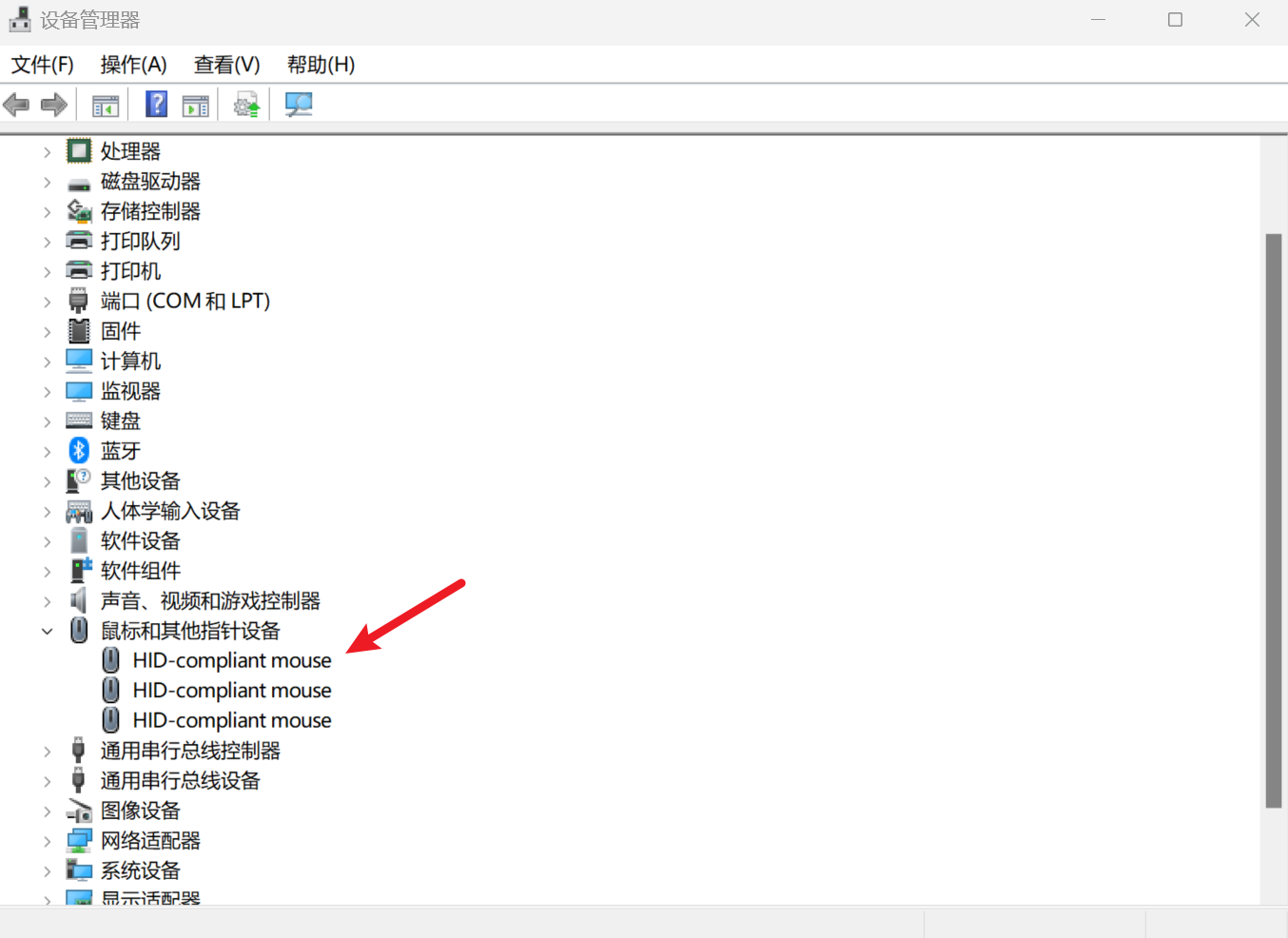
2.2 功能测试
新建测试程序hid.py:
HID 测试程序
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# absolute-hid.py - Test absolute HID mouse
import time
import struct
import os
HID_DEVICE = "/dev/hidg0"
# 检查设备是否存在
if not os.path.exists(HID_DEVICE):
print(f"Error: {HID_DEVICE} does not exist. Run absolute.sh first.")
exit(1)
# 打开设备
fd = open(HID_DEVICE, "wb")
def send_absolute(x, y, buttons=0):
"""
发送鼠标事件
x, y: 绝对坐标 (0 - 32767)
buttons: 按钮状态 (bit0:left, bit1:right, bit2:middle)
"""
# HID 报告: buttons(1) + X(2) + Y(2)
report = struct.pack('<BHH', buttons, x, y)
fd.write(report)
fd.flush()
try:
# 循环移动鼠标画一个正方形
max_val = 32767
step = 8000
positions = [
(step, step),
(max_val-step, step),
(max_val-step, max_val-step),
(step, max_val-step),
(step, step)
]
while True:
for x, y in positions:
send_absolute(x, y)
time.sleep(0.5)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print("Exiting...")
finally:
fd.close()
运行程序:
python3 hid.py
运行效果:
可以看到鼠标在四边形的四个角移动。
3.实现自动瞄准
3.1 获取视频流进行推理
我们需要从HDMI IN获取视频流,所以在开始前请阅读《应用开发》->《摄像头与显示应用》->《HDMI IN与摄像头》,此章节详细描述了HDMI IN的使用。同时还需要阅读《多媒体应用》->《GStreamer与OpenCV》,此章节详细描述了在OpenCV中使用HDMI IN作为视频流输入。
注意:开始前请提前将HDMI IN连接至主机画面。

开始前请测试HDMI IN是否有数据流,打开终端输入:
baiwen@dshanpi-a1:~$ v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video0 --set-fmt-video=width=1920,height=1080,pixelformat=NV12 --stream-mmap --stream-to=camera.nv12 --stream-count=1
<
如果可以正常获取图像并查看生成的camera.nv12,如果图片正常即HDMI IN接口连接正常。
进入端侧推理目录:
cd ~/Projects/rknn_model_zoo/examples/yolov8/python
修改yolov8.py源码:
视频流yolov8推理源码
import os
import cv2
import sys
import argparse
# add path
realpath = os.path.abspath(__file__)
_sep = os.path.sep
realpath = realpath.split(_sep)
sys.path.append(os.path.join(realpath[0]+_sep, *realpath[1:realpath.index('rknn_model_zoo')+1]))
from py_utils.coco_utils import COCO_test_helper
import numpy as np
OBJ_THRESH = 0.25
NMS_THRESH = 0.45
# The follew two param is for map test
# OBJ_THRESH = 0.001
# NMS_THRESH = 0.65
IMG_SIZE = (640, 640) # (width, height), such as (1280, 736)
CLASSES = ("target")
coco_id_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 27, 28, 31, 32, 33, 34,
35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50, 51, 52, 53, 54, 55, 56, 57, 58, 59, 60, 61, 62, 63,
64, 65, 67, 70, 72, 73, 74, 75, 76, 77, 78, 79, 80, 81, 82, 84, 85, 86, 87, 88, 89, 90]
def filter_boxes(boxes, box_confidences, box_class_probs):
"""Filter boxes with object threshold.
"""
box_confidences = box_confidences.reshape(-1)
candidate, class_num = box_class_probs.shape
class_max_score = np.max(box_class_probs, axis=-1)
classes = np.argmax(box_class_probs, axis=-1)
_class_pos = np.where(class_max_score* box_confidences >= OBJ_THRESH)
scores = (class_max_score* box_confidences)[_class_pos]
boxes = boxes[_class_pos]
classes = classes[_class_pos]
return boxes, classes, scores
def nms_boxes(boxes, scores):
"""Suppress non-maximal boxes.
# Returns
keep: ndarray, index of effective boxes.
"""
x = boxes[:, 0]
y = boxes[:, 1]
w = boxes[:, 2] - boxes[:, 0]
h = boxes[:, 3] - boxes[:, 1]
areas = w * h
order = scores.argsort()[::-1]
keep = []
while order.size > 0:
i = order[0]
keep.append(i)
xx1 = np.maximum(x[i], x[order[1:]])
yy1 = np.maximum(y[i], y[order[1:]])
xx2 = np.minimum(x[i] + w[i], x[order[1:]] + w[order[1:]])
yy2 = np.minimum(y[i] + h[i], y[order[1:]] + h[order[1:]])
w1 = np.maximum(0.0, xx2 - xx1 + 0.00001)
h1 = np.maximum(0.0, yy2 - yy1 + 0.00001)
inter = w1 * h1
ovr = inter / (areas[i] + areas[order[1:]] - inter)
inds = np.where(ovr <= NMS_THRESH)[0]
order = order[inds + 1]
keep = np.array(keep)
return keep
def dfl(position):
# Distribution Focal Loss (DFL)
#import torch
#x = torch.tensor(position)
#n,c,h,w = x.shape
#p_num = 4
#mc = c//p_num
#y = x.reshape(n,p_num,mc,h,w)
#y = y.softmax(2)
#acc_metrix = torch.tensor(range(mc)).float().reshape(1,1,mc,1,1)
#y = (y*acc_metrix).sum(2)
#return y.numpy()
n, c, h, w = position.shape
p_num = 4
mc = c // p_num
# [N, 4, mc, H, W]
y = position.reshape(n, p_num, mc, h, w)
# softmax over mc
exp_x = np.exp(y - np.max(y, axis=2, keepdims=True))
y = exp_x / np.sum(exp_x, axis=2, keepdims=True)
# 加权平均 (等价于 torch.arange(mc))
acc_matrix = np.arange(mc, dtype=np.float32).reshape(1, 1, mc, 1, 1)
y = (y * acc_matrix).sum(axis=2) # [N, 4, H, W]
return y
def box_process(position):
grid_h, grid_w = position.shape[2:4]
col, row = np.meshgrid(np.arange(0, grid_w), np.arange(0, grid_h))
col = col.reshape(1, 1, grid_h, grid_w)
row = row.reshape(1, 1, grid_h, grid_w)
grid = np.concatenate((col, row), axis=1)
stride = np.array([IMG_SIZE[1]//grid_h, IMG_SIZE[0]//grid_w]).reshape(1,2,1,1)
position = dfl(position)
box_xy = grid +0.5 -position[:,0:2,:,:]
box_xy2 = grid +0.5 +position[:,2:4,:,:]
xyxy = np.concatenate((box_xy*stride, box_xy2*stride), axis=1)
return xyxy
def post_process(input_data):
boxes, scores, classes_conf = [], [], []
defualt_branch=3
pair_per_branch = len(input_data)//defualt_branch
# Python 忽略 score_sum 输出
for i in range(defualt_branch):
boxes.append(box_process(input_data[pair_per_branch*i]))
classes_conf.append(input_data[pair_per_branch*i+1])
scores.append(np.ones_like(input_data[pair_per_branch*i+1][:,:1,:,:], dtype=np.float32))
def sp_flatten(_in):
ch = _in.shape[1]
_in = _in.transpose(0,2,3,1)
return _in.reshape(-1, ch)
boxes = [sp_flatten(_v) for _v in boxes]
classes_conf = [sp_flatten(_v) for _v in classes_conf]
scores = [sp_flatten(_v) for _v in scores]
boxes = np.concatenate(boxes)
classes_conf = np.concatenate(classes_conf)
scores = np.concatenate(scores)
# filter according to threshold
boxes, classes, scores = filter_boxes(boxes, scores, classes_conf)
# nms
nboxes, nclasses, nscores = [], [], []
for c in set(classes):
inds = np.where(classes == c)
b = boxes[inds]
c = classes[inds]
s = scores[inds]
keep = nms_boxes(b, s)
if len(keep) != 0:
nboxes.append(b[keep])
nclasses.append(c[keep])
nscores.append(s[keep])
if not nclasses and not nscores:
return None, None, None
boxes = np.concatenate(nboxes)
classes = np.concatenate(nclasses)
scores = np.concatenate(nscores)
return boxes, classes, scores
def draw(image, boxes, scores, classes):
for box, score, cl in zip(boxes, scores, classes):
top, left, right, bottom = [int(_b) for _b in box]
print("%s @ (%d %d %d %d) %.3f" % (CLASSES[cl], top, left, right, bottom, score))
cv2.rectangle(image, (top, left), (right, bottom), (255, 0, 0), 2)
cv2.putText(image, '{0} {1:.2f}'.format(CLASSES[cl], score),
(top, left - 6), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.6, (0, 0, 255), 2)
def setup_model(args):
model_path = args.model_path
if model_path.endswith('.pt') or model_path.endswith('.torchscript'):
platform = 'pytorch'
from py_utils.pytorch_executor import Torch_model_container
model = Torch_model_container(args.model_path)
elif model_path.endswith('.rknn'):
platform = 'rknn'
from py_utils.rknn_executor import RKNN_model_container
model = RKNN_model_container(args.model_path, args.target, args.device_id)
elif model_path.endswith('onnx'):
platform = 'onnx'
from py_utils.onnx_executor import ONNX_model_container
model = ONNX_model_container(args.model_path)
else:
assert False, "{} is not rknn/pytorch/onnx model".format(model_path)
print('Model-{} is {} model, starting val'.format(model_path, platform))
return model, platform
def img_check(path):
img_type = ['.jpg', '.jpeg', '.png', '.bmp']
for _type in img_type:
if path.endswith(_type) or path.endswith(_type.upper()):
return True
return False
if __name__ == '__main__':
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='YOLOv8-Seg Real-time Demo')
parser.add_argument('--model_path', type=str, required=True,
help='model path, could be .pt or .rknn file')
parser.add_argument('--target', type=str, default='rk3566',
help='target RKNPU platform')
parser.add_argument('--device_id', type=str, default=None,
help='device id')
args = parser.parse_args()
# 1. 初始化模型
model, platform = setup_model(args)
print('Model ready.')
# 2. 打开摄像头
#cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0,cv2.CAP_V4L2)
cap = cv2.VideoCapture("v4l2src device=/dev/video0 ! videoconvert ! appsink", cv2.CAP_GSTREAMER)
if not cap.isOpened():
print('Cannot open camera.')
exit(-1)
# 3. 实时循环
while True:
ret, frame = cap.read()
if not ret:
break
h0, w0 = frame.shape[:2]
# 3-1 LetterBox 预处理
co_helper = COCO_test_helper(enable_letter_box=True)
img = co_helper.letter_box(frame.copy(), IMG_SIZE, pad_color=(0, 0, 0))
img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
img = np.expand_dims(img, 0)
# 3-2 构造输入
if platform in ['pytorch', 'onnx']:
input_data = img.transpose(2, 0, 1).astype(np.float32) / 255.
input_data = np.expand_dims(input_data, 0)
else:
input_data = img
# 3-3 推理
outputs = model.run([input_data])
boxes, classes, scores = post_process(outputs)
# 3-4 画框
vis = frame.copy()
if boxes is not None:
boxes_real = co_helper.get_real_box(boxes)
draw(vis, boxes_real, scores, classes)
# 3-5 实时显示
cv2.imshow('YOLOv8', vis)
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
cap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
model.release()
运行程序获取:
python3 yolov8.py --model_path ../model/yolov8.rknn --target rk3576
运行后 HDMI OUT的电脑端可打开一张数据集的图片。
3.2 自瞄源码示例
yolov8+hid源码
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import os
import cv2
import sys
import argparse
import struct
import time
import numpy as np
# --------------------------------------------------
# Path setup (robust search for 'rknn_model_zoo')
# --------------------------------------------------
def append_model_zoo_root():
try:
here = os.path.abspath(os.path.dirname(__file__))
except NameError:
here = os.getcwd()
root = here
found = False
while True:
parent = os.path.dirname(root)
if os.path.basename(root) == 'rknn_model_zoo':
found = True
break
if parent == root:
break
root = parent
if found:
sys.path.append(root)
else:
print("Warning: 'rknn_model_zoo' not found in ancestors; relying on installed packages.")
append_model_zoo_root()
from py_utils.coco_utils import COCO_test_helper
# --------------------------------------------------
# Config
# --------------------------------------------------
OBJ_THRESH = 0.25
NMS_THRESH = 0.45
IMG_SIZE = (640, 640)
CLASSES = ("target",)
SCREEN_W, SCREEN_H = 1920, 1080
# Aim smoothing
SMOOTH_FACTOR = 0 # 0.5–0.9; lower = more responsive
DEADZONE = 2 # Deadzone (pixels)
AIM_STEP = 0.1 # Fraction per frame to move toward target (0–1)
CENTER_THRESH = 12 # Pixel threshold to consider centered (for click)
SEND_COOLDOWN = 0.08 # Min interval between position reports (seconds)
POS_EPS_PX = 2 # Position change threshold (px); below = do not send
# Click cooldown
CLICK_COOLDOWN = 0.35 # Min interval between clicks (seconds)
# Absolute HID report range
ABS_MAX = 32767
# --------------------------------------------------
# HID mouse (absolute mode: <BHH>)
# --------------------------------------------------
def _clip_abs(v: int) -> int:
return max(0, min(ABS_MAX, int(v)))
def pixels_to_abs(x_px: int, y_px: int, screen_w=SCREEN_W, screen_h=SCREEN_H):
"""
Pixel coordinates (0..W-1, 0..H-1) → absolute coordinates (0..32767).
Use (N-1) in the denominator so the max pixel maps to ABS_MAX.
"""
ax = round(x_px * ABS_MAX / max(1, (screen_w - 1)))
ay = round(y_px * ABS_MAX / max(1, (screen_h - 1)))
return _clip_abs(ax), _clip_abs(ay)
def move_mouse_to(hid_fd, target_x_px, target_y_px, screen_w, screen_h, cur_pos, horizontal_only=False):
"""
Move the mouse to screen pixel coordinates (absolute reports).
cur_pos: current screen pixel position (tracking only; not sent in the report)
"""
cx, cy = cur_pos
tx, ty = int(target_x_px), int(target_y_px)
if horizontal_only:
ty = cy
if hid_fd is None:
mode = "H-ONLY" if horizontal_only else "FULL"
print(f"[SIM] move [{mode}] cur=({cx},{cy}) -> tgt=({tx},{ty})")
return (tx, ty)
ax, ay = pixels_to_abs(tx, ty, screen_w, screen_h)
try:
# buttons=0 (move only; no click)
report = struct.pack('<BHH', 0x00, ax, ay)
hid_fd.write(report)
hid_fd.flush()
return (tx, ty)
except Exception as e:
print(f"Mouse move failed: {e}")
return (cx, cy)
def click_mouse(hid_fd, at_x_px: int, at_y_px: int, screen_w=SCREEN_W, screen_h=SCREEN_H, press_ms=100, retries=0):
"""
Absolute-position click: requires screen pixel coordinates.
- press_ms: hold duration in milliseconds
- retries: retry attempts for transient write failures
"""
if hid_fd is None:
print(f"[SIM] click at ({at_x_px},{at_y_px})")
return
ax, ay = pixels_to_abs(int(at_x_px), int(at_y_px), screen_w, screen_h)
for attempt in range(retries + 1):
try:
# Left button down (bit0=1) with coordinates
hid_fd.write(struct.pack('<BHH', 0x01, ax, ay))
hid_fd.flush()
time.sleep(press_ms / 1000.0)
# Left button up
hid_fd.write(struct.pack('<BHH', 0x00, ax, ay))
hid_fd.flush()
return
except Exception as e:
print(f"Mouse click failed (attempt {attempt+1}): {e}")
time.sleep(0.02)
# --------------------------------------------------
# Post-processing helpers
# --------------------------------------------------
def filter_boxes(boxes, box_confidences, box_class_probs):
# boxes: (N,4) xyxy
# box_confidences: (N,) or (N,1..)
# box_class_probs: (N,C)
box_confidences = box_confidences.reshape(-1)
class_max_score = np.max(box_class_probs, axis=-1)
classes = np.argmax(box_class_probs, axis=-1)
mask = class_max_score * box_confidences >= OBJ_THRESH
scores = (class_max_score * box_confidences)[mask]
return boxes[mask], classes[mask], scores
def nms_boxes(boxes, scores, iou_thr=NMS_THRESH):
if boxes.size == 0:
return np.array([], dtype=np.int64)
x1, y1 = boxes[:, 0], boxes[:, 1]
x2, y2 = boxes[:, 2], boxes[:, 3]
areas = np.maximum(0, x2 - x1) * np.maximum(0, y2 - y1)
order = scores.argsort()[::-1]
keep = []
while order.size > 0:
i = order[0]
keep.append(i)
xx1 = np.maximum(x1[i], x1[order[1:]])
yy1 = np.maximum(y1[i], y1[order[1:]])
xx2 = np.minimum(x2[i], x2[order[1:]])
yy2 = np.minimum(y2[i], y2[order[1:]])
inter = np.maximum(0.0, xx2 - xx1) * np.maximum(0.0, yy2 - yy1)
iou = inter / (areas[i] + areas[order[1:]] - inter + 1e-9)
inds = np.where(iou <= iou_thr)[0]
order = order[inds + 1]
return np.array(keep, dtype=np.int64)
def dfl(position):
# position: (n,c,h,w), where c = 4 * mc
n, c, h, w = position.shape
p_num = 4
mc = c // p_num
y = position.reshape(n, p_num, mc, h, w)
exp_y = np.exp(y - np.max(y, axis=2, keepdims=True))
y = exp_y / np.sum(exp_y, axis=2, keepdims=True)
acc = np.arange(mc, dtype=np.float32).reshape(1, 1, mc, 1, 1)
return (y * acc).sum(axis=2) # (n, 4, h, w)
def box_process(position):
# position: (n,c,h,w) where c contains 4 DFL components
n, c, h, w = position.shape
col, row = np.meshgrid(np.arange(w), np.arange(h))
grid = np.concatenate([col.reshape(1, 1, h, w), row.reshape(1, 1, h, w)], axis=1)
stride = np.array([IMG_SIZE[1] // h, IMG_SIZE[0] // w]).reshape(1, 2, 1, 1)
position = dfl(position) # (n,4,h,w) distances [left, top, right, bottom]
xy1 = grid + 0.5 - position[:, :2]
xy2 = grid + 0.5 + position[:, 2:4]
xyxy = np.concatenate([xy1 * stride, xy2 * stride], axis=1) # (n,4,h,w)
return xyxy
def post_process(input_data):
"""
Based on the "3-branch + DFL" assumption:
input_data is ordered per branch: [box_head0, cls_head0, box_head1, cls_head1, box_head2, cls_head2, ...]
If your model outputs differ, adapt here to:
- decode per-cell xyxy (in the network input coordinate system)
- obtain class logits/probabilities
- object/confidence (use 1 if there is no explicit objectness head)
"""
if input_data is None or len(input_data) == 0:
return None, None, None
# Try splitting into 3 branches by default
branches = 3
per_branch = max(1, len(input_data) // branches)
boxes_list, scores_list, classes_conf_list = [], [], []
def flatten(x):
# (n,c,h,w) -> (h*w, c) (n is usually 1 here)
if x.ndim == 4:
x = np.squeeze(x, axis=0)
x = x.transpose(1, 2, 0).reshape(-1, x.shape[0])
elif x.ndim == 3:
x = x.transpose(1, 2, 0).reshape(-1, x.shape[0])
elif x.ndim == 2:
pass
else:
x = x.reshape(x.shape[0], -1)
return x
try:
for i in range(branches):
box_head = input_data[per_branch * i]
cls_head = input_data[min(per_branch * i + 1, len(input_data)-1)]
# box_head: (1,4*mc,h,w) → decode to (1,4,h,w), then flatten to (H*W,4)
xyxy = box_process(box_head) # (1,4,h,w)
xyxy = np.squeeze(xyxy, axis=0) # (4,h,w)
xyxy = xyxy.transpose(1, 2, 0).reshape(-1, 4) # (H*W,4)
# cls_head: (1,C,h,w) or (1,(obj+cls),h,w); assume per-class scores here
cls_flat = flatten(cls_head) # (H*W, C)
# If there is no objectness head, use ones as placeholders
obj = np.ones((cls_flat.shape[0], 1), dtype=cls_flat.dtype)
boxes_list.append(xyxy)
classes_conf_list.append(cls_flat)
scores_list.append(obj)
boxes = np.concatenate(boxes_list, axis=0) if boxes_list else None
classes_conf = np.concatenate(classes_conf_list, axis=0) if classes_conf_list else None
scores = np.concatenate(scores_list, axis=0) if scores_list else None
if boxes is None or classes_conf is None or scores is None:
return None, None, None
boxes, classes, scores = filter_boxes(boxes, scores, classes_conf)
if boxes.size == 0:
return None, None, None
nboxes, nclasses, nscores = [], [], []
for c in set(classes.tolist()):
idx = np.where(classes == c)[0]
b, s = boxes[idx], scores[idx]
keep = nms_boxes(b, s)
if keep.size:
nboxes.append(b[keep])
nclasses.append(classes[idx][keep])
nscores.append(s[keep])
if not nboxes:
return None, None, None
return np.concatenate(nboxes), np.concatenate(nclasses), np.concatenate(nscores)
except Exception as e:
print(f"post_process failed: {e}")
return None, None, None
def draw(image, boxes, scores, classes):
"""
boxes: (N,4) in xyxy (x1,y1,x2,y2) on original image coordinates
"""
for box, score, cl in zip(boxes, scores, classes):
x1, y1, x2, y2 = map(int, box)
name = CLASSES[cl] if cl < len(CLASSES) else str(cl)
print(f"{name} @ ({x1},{y1},{x2},{y2}) {score:.3f}")
cv2.rectangle(image, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), (255, 0, 0), 2)
cv2.putText(image, f"{name} {score:.2f}", (x1, max(0, y1 - 6)),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.6, (0, 0, 255), 2)
# --------------------------------------------------
# Utility
# --------------------------------------------------
def map_to_screen(cx, cy, img_w, img_h, screen_w, screen_h):
# Convert image pixel coordinates (model-input or original image) to screen pixel coordinates
sx = int(round(cx * screen_w / img_w))
sy = int(round(cy * screen_h / img_h))
return sx, sy
def setup_model(args):
path = args.model_path
if path.endswith(('.pt', '.torchscript')):
from py_utils.pytorch_executor import Torch_model_container
return Torch_model_container(path), 'pytorch'
elif path.endswith('.rknn'):
from py_utils.rknn_executor import RKNN_model_container
return RKNN_model_container(path, args.target, args.device_id), 'rknn'
elif path.endswith('.onnx'):
from py_utils.onnx_executor import ONNX_model_container
return ONNX_model_container(path), 'onnx'
else:
raise ValueError(f"{path} is not a supported model")
# --------------------------------------------------
# Main
# --------------------------------------------------
def main():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='YOLOv8 real-time aimbot (absolute HID)')
parser.add_argument('--model_path', required=True, help='.pt / .rknn / .onnx')
parser.add_argument('--target', default='rk3566', help='RKNPU target')
parser.add_argument('--device_id', default=None)
parser.add_argument('--horizontal_test', action='store_true', help='only X axis')
parser.add_argument('--camera', default="v4l2src device=/dev/video0 ! videoconvert ! appsink",
help='GStreamer pipeline or numeric camera index')
args = parser.parse_args()
# HID device open (absolute mode)
try:
mouse_fd = open("/dev/hidg0", "wb")
print("Mouse device initialized (absolute HID)")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Mouse device init failed: {e}")
print("Running in simulation mode")
mouse_fd = None
# Model
model, platform = setup_model(args)
print('Model ready:', platform)
# Camera
if args.camera.isdigit():
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(int(args.camera))
else:
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(args.camera, cv2.CAP_GSTREAMER)
if not cap.isOpened():
print('Failed to open camera')
sys.exit(-1)
# LetterBox helper (instantiate once outside the loop)
co_helper = COCO_test_helper(enable_letter_box=True)
# Current mouse pixel position (tracking only)
cur_mouse = (SCREEN_W // 2, SCREEN_H // 2)
last_target = None
last_send_time = 0.0
last_sent_pos = None # (x, y) in screen pixels
last_click_time = 0.0
last_good_target = None # Last valid target in screen pixels
try:
while True:
ret, frame = cap.read()
if not ret:
print("Camera read failed")
break
h0, w0 = frame.shape[:2]
# ---- Preprocess (letterbox to IMG_SIZE) ----
lb_img = co_helper.letter_box(frame, IMG_SIZE, pad_color=(0, 0, 0))
rgb = cv2.cvtColor(lb_img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
inp = np.expand_dims(rgb, 0) # (1,H,W,3)
# Some RKNN containers normalize internally; switch here if you want a unified path
if platform in ['pytorch', 'onnx']:
input_data = inp.transpose(0, 3, 1, 2).astype(np.float32) / 255.0
else:
input_data = inp # Keep as-is if RKNN container handles normalization internally
# ---- Inference ----
outputs = model.run([input_data])
# ---- Post-process ----
boxes, classes, scores = post_process(outputs)
vis = frame.copy()
if boxes is not None and len(boxes):
# Map boxes back to original frame coordinates
boxes_real = co_helper.get_real_box(boxes)
draw(vis, boxes_real, scores, classes)
# Pick a target (highest score)
best_idx = int(np.argmax(scores))
x1, y1, x2, y2 = boxes_real[best_idx]
cx = (x1 + x2) / 2.0
cy = (y1 + y2) / 2.0
# Image coords → screen pixel coords
target_x, target_y = map_to_screen(cx, cy, w0, h0, SCREEN_W, SCREEN_H)
# Exponential moving average smoothing
if last_target is None:
smoothed_target = (target_x, target_y)
else:
smoothed_target = (
last_target[0] * SMOOTH_FACTOR + target_x * (1 - SMOOTH_FACTOR),
last_target[1] * SMOOTH_FACTOR + target_y * (1 - SMOOTH_FACTOR)
)
last_target = smoothed_target
target_x, target_y = smoothed_target
last_good_target = (target_x, target_y) # Record after smoothing
# Step from current mouse position toward target by a ratio
screen_cx, screen_cy = SCREEN_W // 2, SCREEN_H // 2 # You can use cur_mouse as the origin if preferred
dx = target_x - screen_cx
dy = target_y - screen_cy
dist = np.hypot(dx, dy)
if dist < 30:
AIM_STEP = 0.05
elif dist < 80:
AIM_STEP = 0.10
else:
AIM_STEP = np.clip(dist / 1550, 0.1, 0.12)
# Deadzone to ignore tiny jitters
if abs(dx) < DEADZONE and abs(dy) < DEADZONE:
pass # No movement
else:
# (1) Compute next screen pixel position (step + clamp to bounds)
move_x = int(round(cur_mouse[0] + dx * AIM_STEP))
move_y = int(round(cur_mouse[1] + dy * AIM_STEP))
move_x = max(0, min(SCREEN_W - 1, move_x))
move_y = max(0, min(SCREEN_H - 1, move_y))
# (2) Debounce + cooldown before sending report
now = time.time()
pos_changed = (
last_sent_pos is None or
abs(move_x - last_sent_pos[0]) > POS_EPS_PX or
abs(move_y - last_sent_pos[1]) > POS_EPS_PX
)
if pos_changed and (now - last_send_time) >= SEND_COOLDOWN:
cur_mouse = move_mouse_to(
mouse_fd, move_x, move_y, SCREEN_W, SCREEN_H, cur_mouse,
horizontal_only=args.horizontal_test
)
last_send_time = now
last_sent_pos = (move_x, move_y)
box_w = x2 - x1
box_h = y2 - y1
CENTER_THRESH = max(8, min(15, (box_w + box_h) / 4))
if abs(dx) < CENTER_THRESH and abs(dy) < CENTER_THRESH:
print(f"[DEBUG] Entered click window dx={dx:.1f} dy={dy:.1f}")
now = time.time()
if now - last_click_time >= CLICK_COOLDOWN:
print("[DEBUG] Cooldown passed, FIRE")
click_mouse(mouse_fd, int(cur_mouse[0]), int(cur_mouse[1]))
last_click_time = now
else:
print("No target detected, skip mouse move.")
cv2.imshow('YOLOv8', vis)
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
finally:
cap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
try:
model.release()
except Exception:
pass
if mouse_fd:
mouse_fd.close()
print("Mouse device closed")
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
由于不同的电脑运行程序后效果可能会有所差异,可通过调整下面几个参数来实现较优效果
SMOOTH_FACTOR:目标坐标指数平滑系数。
DEADZONE:像素死区,小于该距离不移动,用于抑制轻微抖动。
AIM_STEP:每帧朝目标移动的比例,上限越大移动越快,易冲过目标。
CENTER_THRESH:判定“已居中”的像素半径,大于该值不触发点击。
SEND_COOLDOWN:连续两次 HID 坐标报告的最小时间间隔,越短越流畅。
POS_EPS_PX:位置变化阈值,低于该像素差不再发送报告,防止微抖。
如果出现移动过头或者摇头晃脑的状态,可调节AIM_STEP参数
AIM_STEP = np.clip(dist / 1550, 0.1, 0.12)
分母 1550:数值越大移动越慢,越小移动越快
下限 0.1:末段最小步长,越小越精细
上限 0.12:大距离最大步长,越小越不易冲过目标
3.3 程序运行
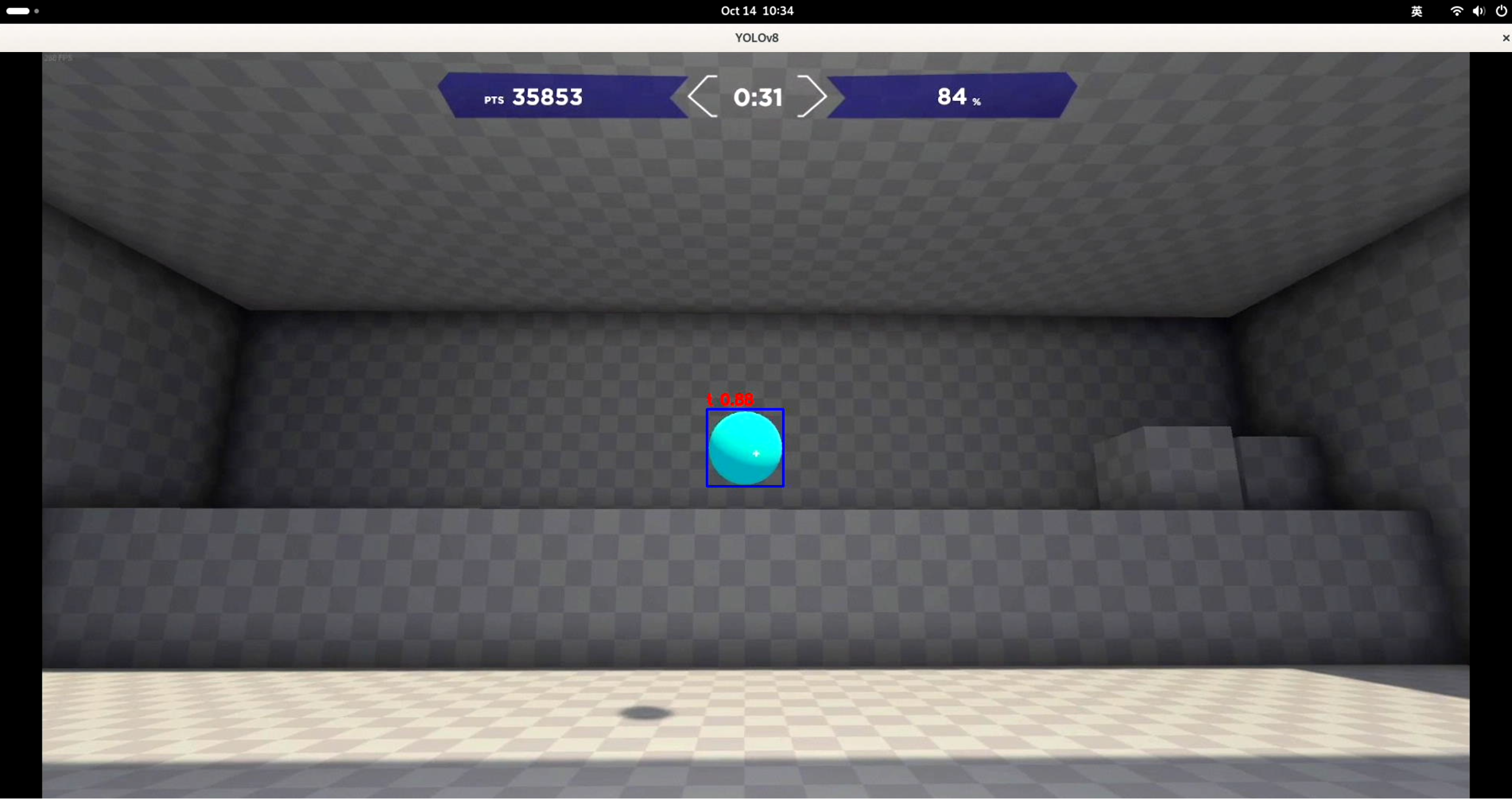
在HDMI OUT的电脑端运行Aim Lab,这里使用任务中的反应射击为例。
打开DshanPI A1的终端执行:
python3 yolov8.py --model ../model/yolov8.rknn
运行效果:

运行成功后,会程序会自动检测目标,并控制鼠标移动至目标区域并射击。